DBBlobEditor - View / Edit / Import / Export Database LOB (BLOB, CLOB) data »
In daily database management, synchronous backup of large object data such as BLOB/CLOB is a high-frequency requirement. Manual operations are not only inefficient but also prone to omissions. DBBlobEditor offers CLI (Command Line Interface) execution capabilities, and when combined with system scheduled tasks, it enables effortless automated and scheduled synchronization of BLOB data, making the migration and backup of large object data more efficient and stable. This article details the full process configuration for achieving scheduled synchronization of database BLOB data through DBBlobEditor's CLI mode, with support for Windows, Linux, and macOS systems.
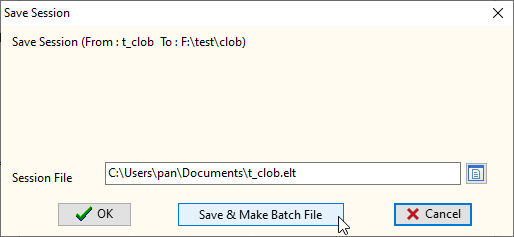
To enable command line execution and scheduled synchronization, you first need to configure the import/export rules for LOB data in the DBBlobEditor graphical interface and save them as a task session—this is the foundation for subsequent CLI execution and scheduled scheduling across all systems.
t_clob to the local path F:\test\clob for Windows, or corresponding paths like /home/user/test/clob for Linux/macOS);C:\Users\pan\Documents\t_clob.elt for Windows, /home/user/Documents/t_clob.elt for Linux/macOS);
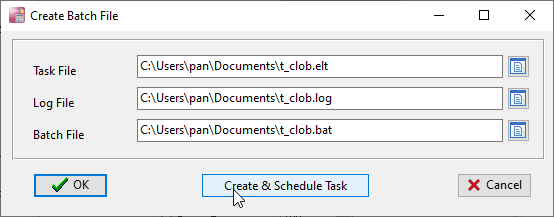
Clicking Save & Make Batch File will bring up the Create Batch File configuration window. The core of this step is to associate the session file and log file, and generate an executable batch file (.bat for Windows) or shell script (.sh for Linux/macOS), facilitating subsequent command line calls and scheduled task execution.
The window provides two core options: OK and Create & Schedule Task. Click OK if you only need to generate the file for manual CLI execution; select Create & Schedule Task if you want to configure scheduled tasks directly. We will explain CLI execution first, then scheduled scheduling configuration.
After clicking OK, the software generates the corresponding executable file in the specified path, which encapsulates the core commands for BLOB data synchronization and lays the groundwork for subsequent operations.
After generating the batch/shell file, you can manually execute the BLOB data synchronization task through the command line of the corresponding system, which is simple, flexible, and suitable for ad-hoc synchronization needs.
C: cd "C:\Users\pan\AppData\Local\Programs\DBBlobEditor"
session parameter and the log file via the logfile parameter:DBBlobEditor session="C:\Users\pan\Documents\t_clob.elt" logfile="C:\Users\pan\Documents\t_clob.log"
chmod +x /home/user/Documents/t_clob.sh
cd /opt/DBBlobEditor
./DBBlobEditor session="/home/user/Documents/t_clob.elt" logfile="/home/user/Documents/t_clob.log"
After running the command, DBBlobEditor will automatically complete the BLOB/CLOB data synchronization according to the configuration in the session file, and the execution process and results will be recorded in the specified log file in real time across all systems.
Manual CLI execution meets ad-hoc needs, and combining it with the built-in scheduled task tools of each system enables automated synchronization strategies such as one-time execution at a specified time and recurring execution daily/weekly, completely freeing up manual work. The software’s Create & Schedule Task option supports direct jump to the system’s scheduled task configuration interface for quick setup, and you can also configure it manually as follows:
Use the Task Scheduler:
Use the crontab tool (the most common scheduled task tool for Linux):
crontab -e
0 2 * * * /opt/DBBlobEditor/DBBlobEditor session="/home/user/Documents/t_clob.elt" logfile="/home/user/Documents/t_clob.log" >> /home/user/Documents/clob_sync_cron.log 2>&1
Use either crontab (same as Linux) or the native Launchd tool:
/Library/LaunchDaemons/ directory, define the execution time and the path of the DBBlobEditor execution command, then load the configuration file via the launchctl command to complete the scheduled task setup.chmod +x, and ensure the executing user has database access rights, file system read/write rights, and execution rights for the DBBlobEditor program;DBBlobEditor's CLI mode, combined with the native scheduled task tools of Windows, Linux, and macOS, provides a highly efficient automated solution for the synchronization of database BLOB/CLOB large object data. From saving task sessions and generating cross-system executable files, to manual CLI execution and scheduled scheduling configuration, the entire process is simple to operate and requires no complex script development, enabling scheduled synchronization and backup of data with ease. Whether for daily database data backup or cross-environment BLOB data migration, this method can greatly improve work efficiency, reduce errors caused by manual operations, and is suitable for database administrators and developers for daily use across all mainstream operating systems.