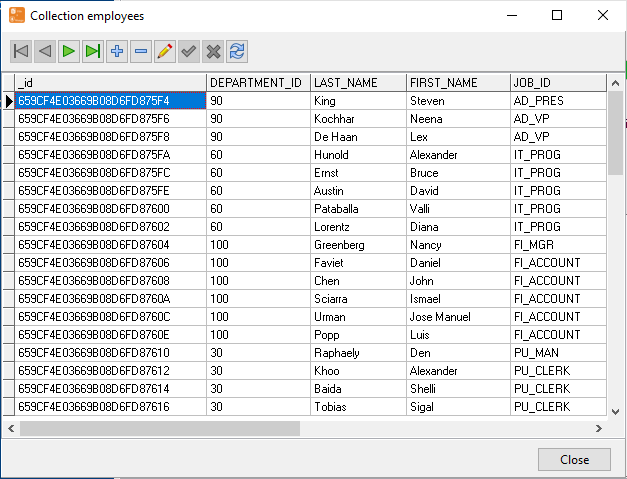
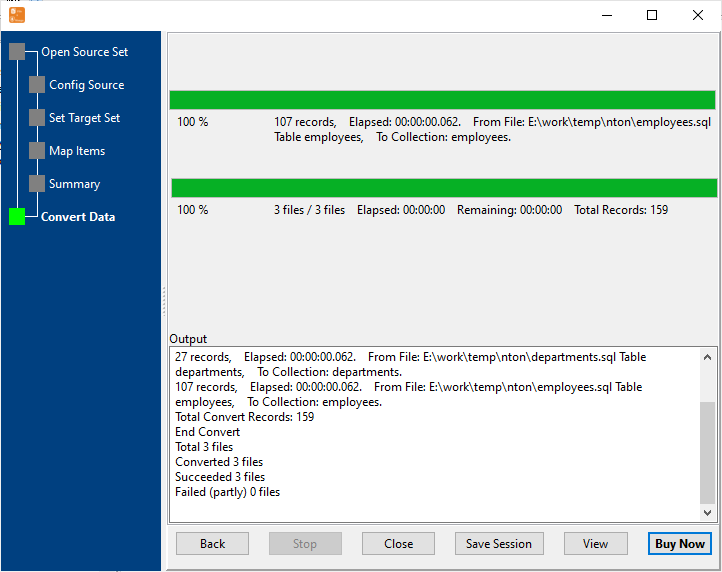
4 Simple Steps to Import SQL to MongoDB Database
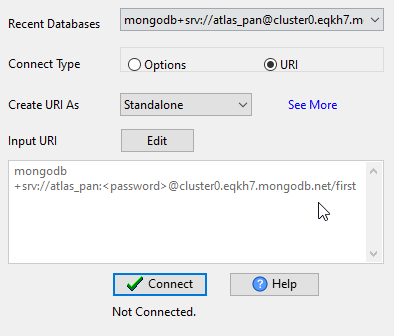
Connect MongoDB
Configure your MongoDB connection details (URI/host:port, authentication) — — supports standalone, replica set, sharded cluster, MongoDB Atlas, and self-hosted servers.
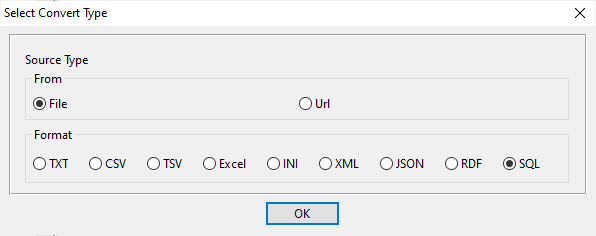
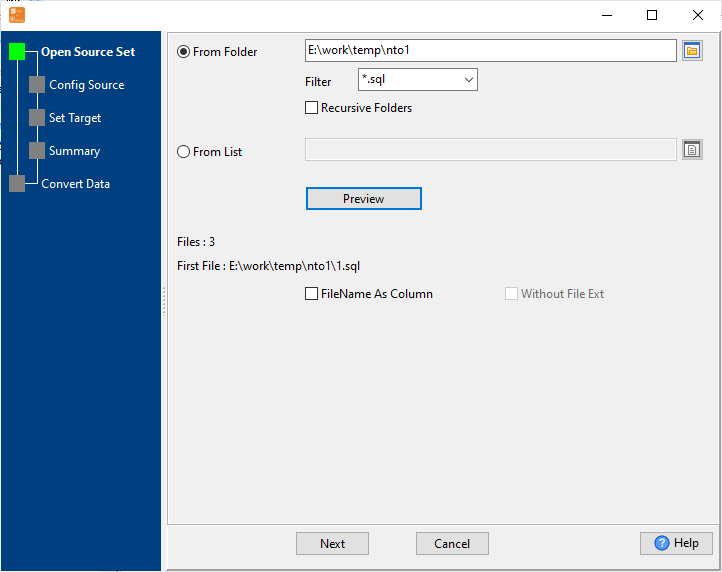
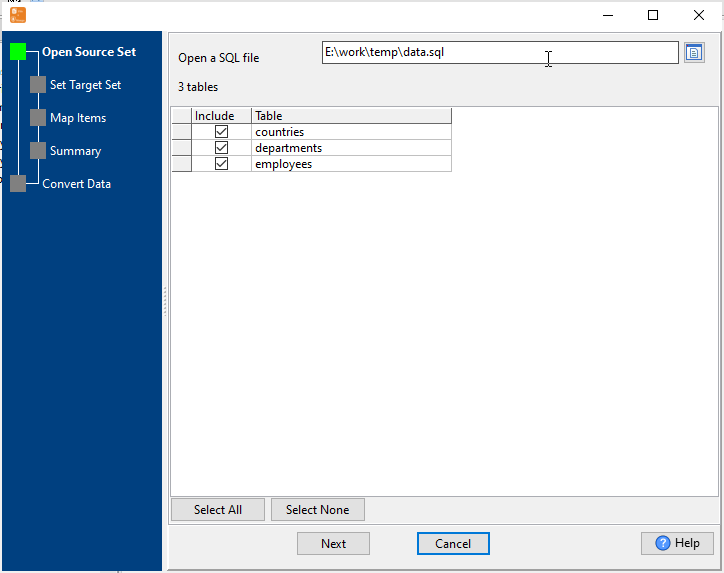
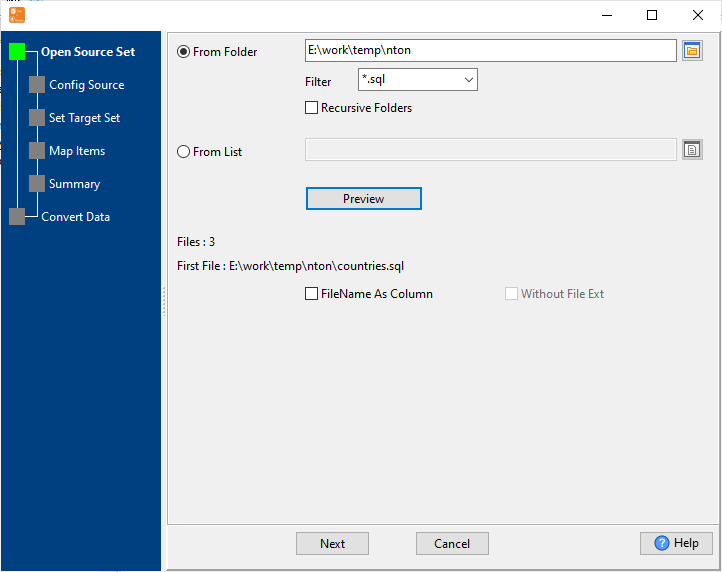
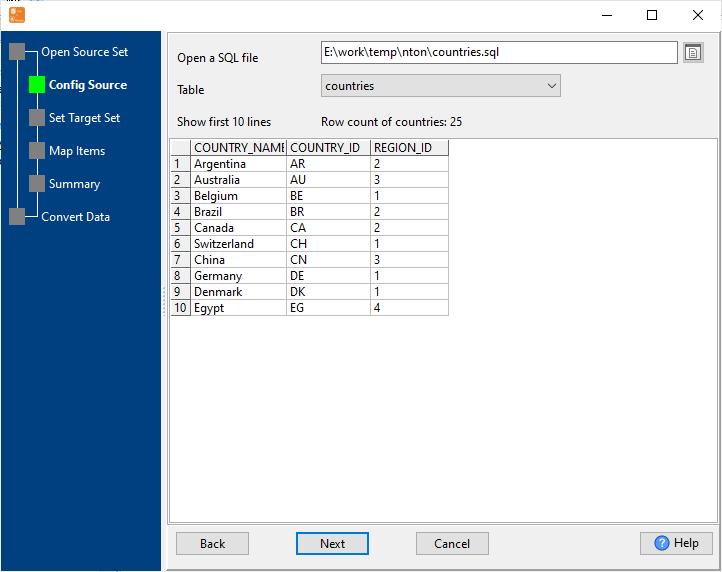
Select SQL Source SQL
Choose your SQL source: local .sql backup files or direct connection to SQL databases: MySQL, Oracle, SQL Server, PostgreSQL, SQLite, DB2, Access, DBF, and more.
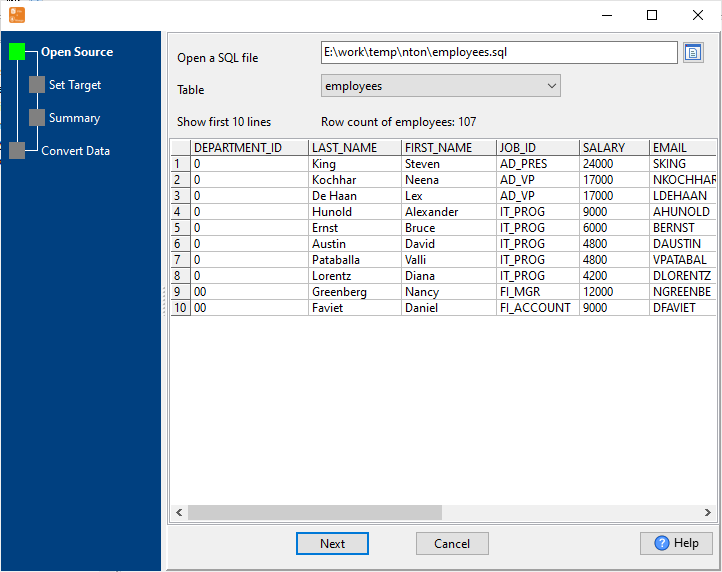
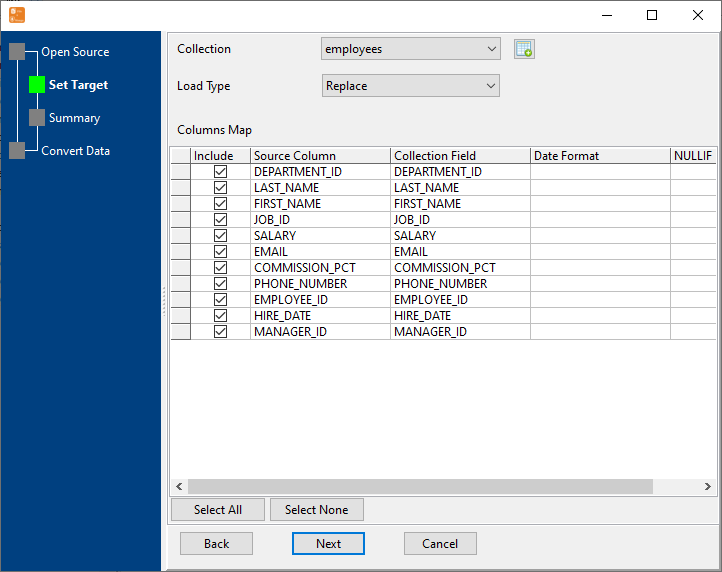
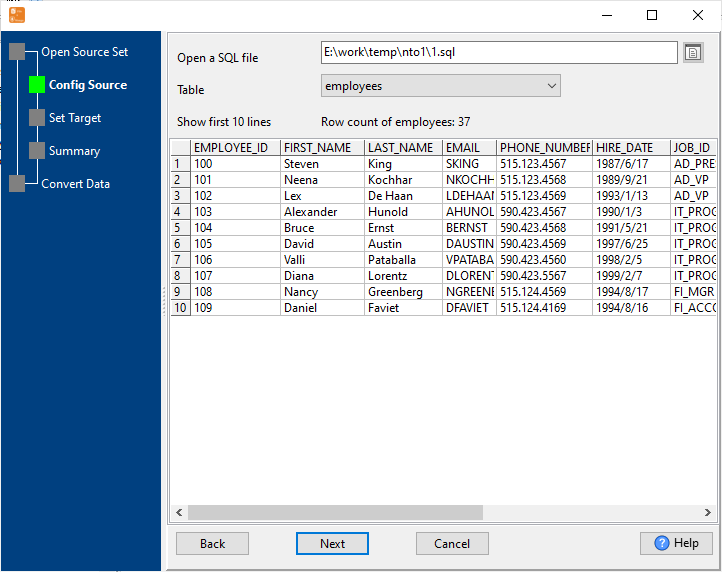
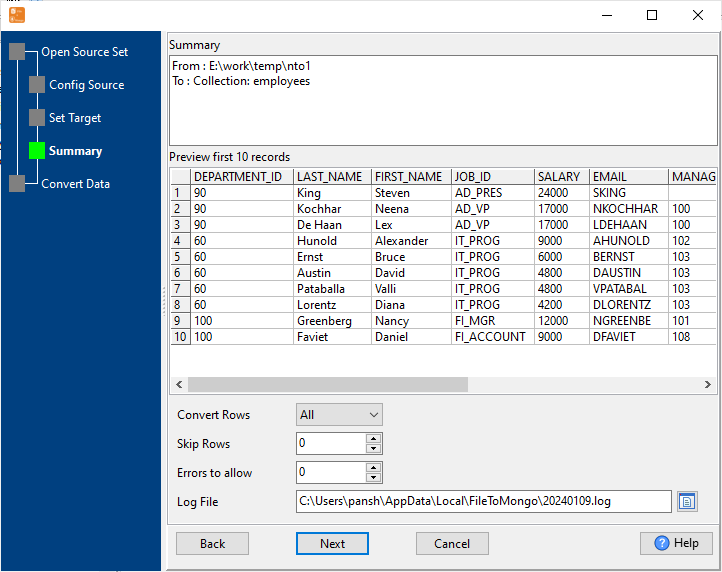
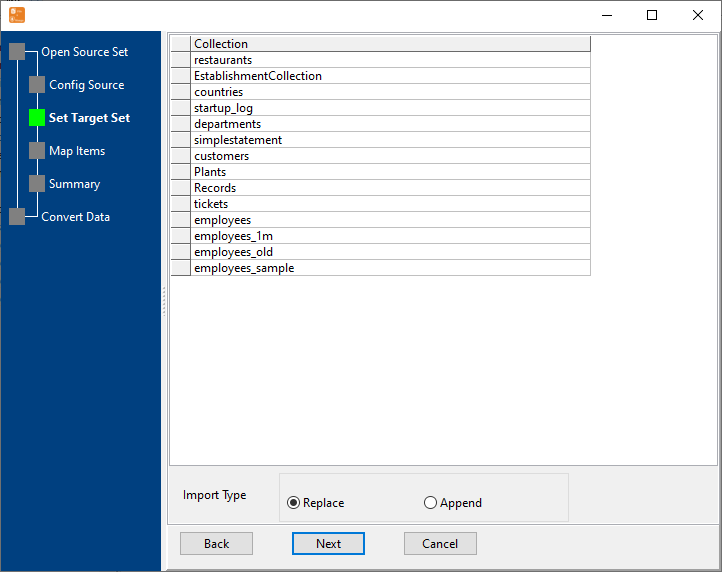
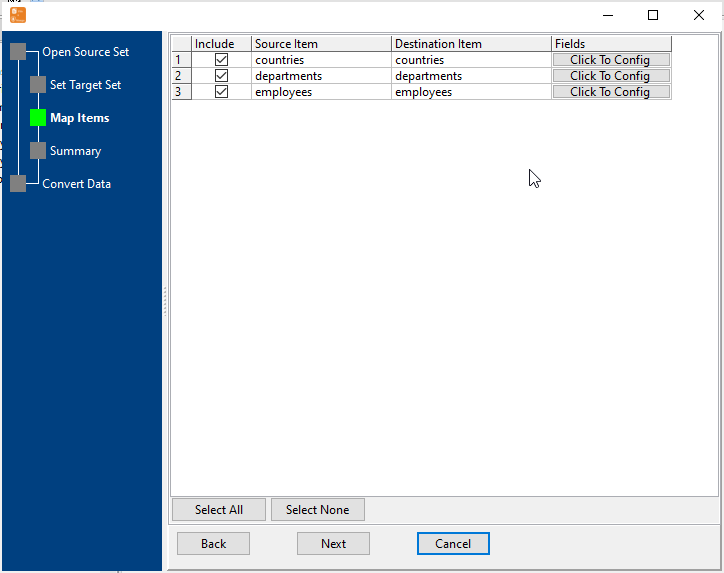
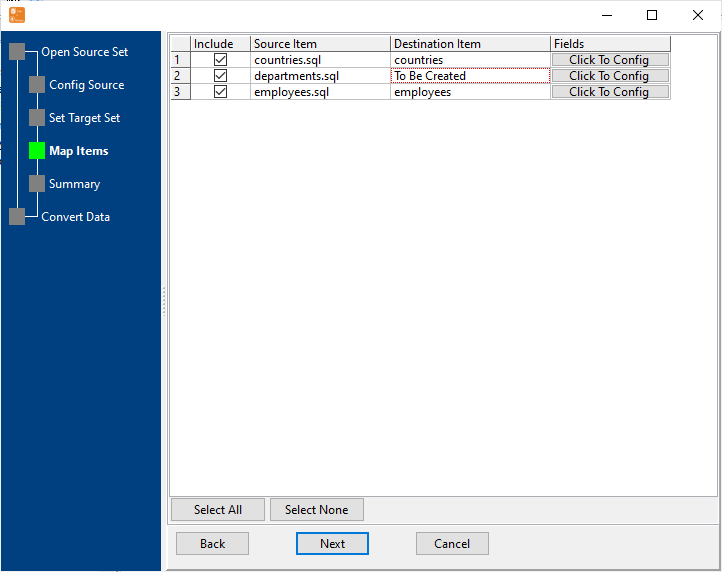
Configure Import Rules Mapping
Set schema mapping (SQL tables ↔ MongoDB collections, SQL columns ↔ MongoDB fields), data type conversion rules, primary key mapping, and duplicate data handling.
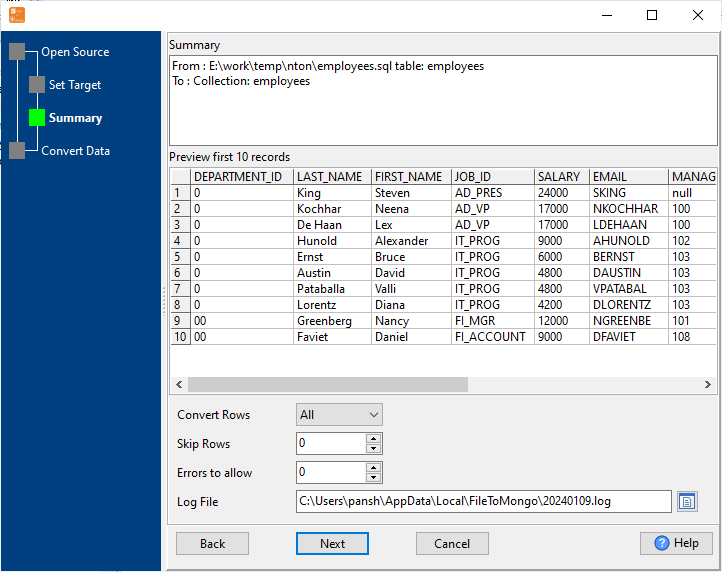
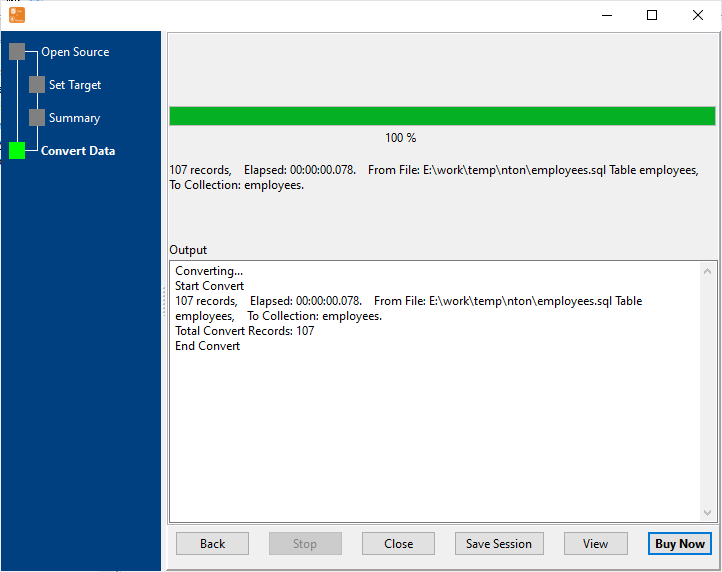
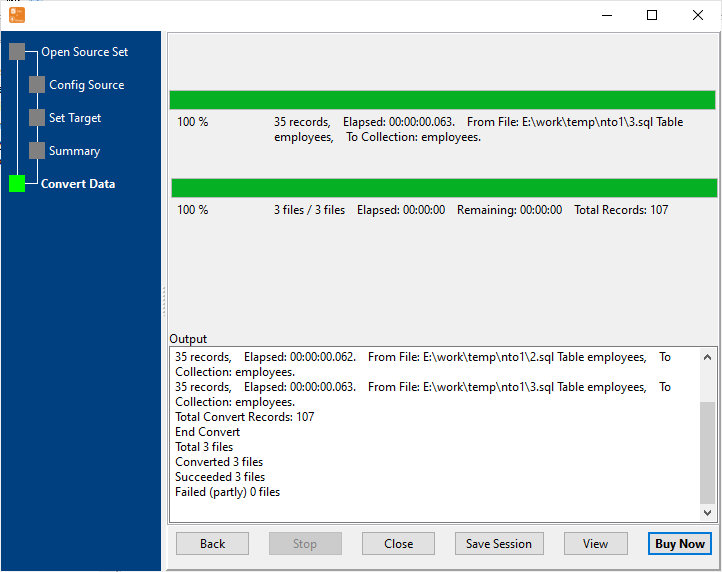
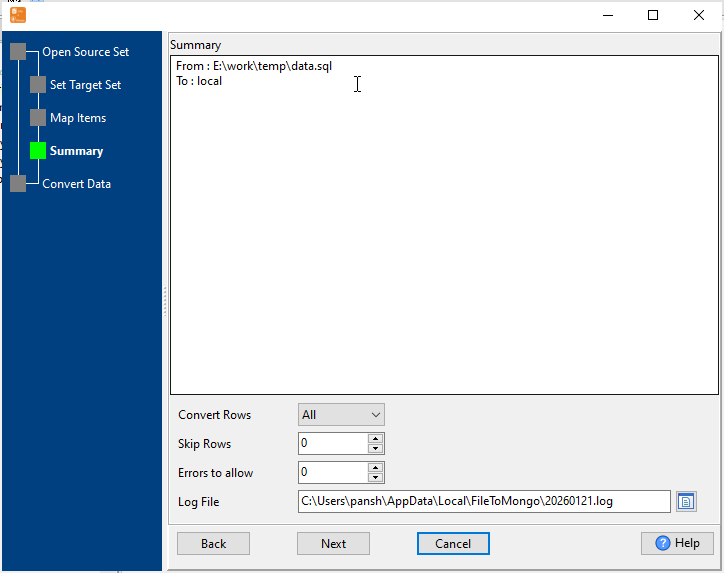
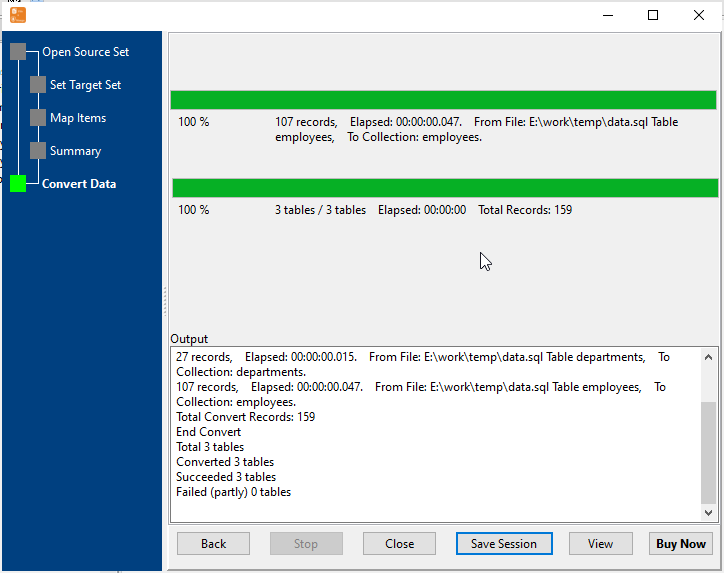
Start SQL Import & View Real-Time Progress
Real-time display of import speed, success/failure count, and error details. Failed rows are marked for easy retry — even for large SQL datasets.
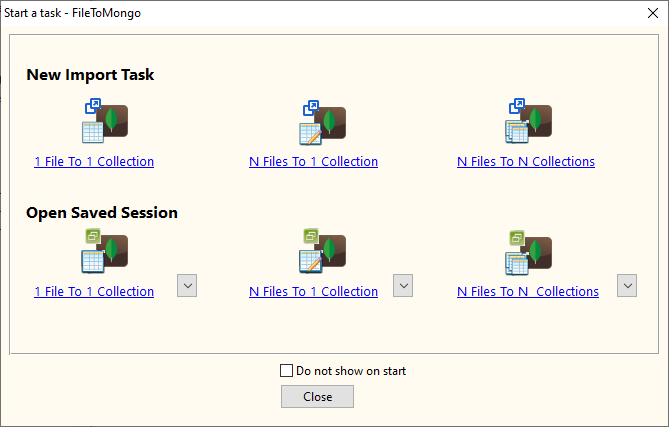
4 Flexible SQL to MongoDB Import Types
Single SQL Table to Single Collection
Connect directly to a SQL database and import one table to one MongoDB collection — perfect for targeted table migration with real-time data.
Example:
MySQL Table: sales.customers → MongoDB Collection: customers
✅ Custom field renaming and data type conversion
Multiple Tables in Multiple SQL Files to Single Collection
Import multiple SQL tables in diffrent SQL files to a Single MongoDB collection in one operation — ideal for merge data from SQL to MongoDB.
Example:
SQL Files: orders_jan.sql (Table: orders), orders_feb.sql (Table: orders) → MongoDB Collection: orders
✅ Auto-parse SQL table structure and map to MongoDB schema
Multiple Tables in 1 SQL File to Multiple Collections
Import a local .sql backup file to MongoDB collections — ideal for migrating a SQL backup file to MongoDB.
Example:
SQL File: sales_2025_backup.sql → MongoDB Collections: products, orders
Multiple Tables in Multiple SQL Files to Multiple Collections
Bulk import multiple SQL tables to corresponding MongoDB collections in one operation — ideal for full database migration from SQL to MongoDB.
Example:
Tables: products.sql (Table: products), orders.sql (Table: orders) → Collections: products, orders
Key Features of SQL to MongoDB Importer
Multi-SQL Database Compatibility
- SQL File Support: .sql backup files from any SQL database, MySQL, Oracle, SQL Server, PostgreSQL, DB2, SQLite, and more
- Cross-version compatibility with legacy SQL databases
High Performance & Scalability
- Huge SQL File Support: Stream processing avoids memory overflow
- Batch Import: Process millions of rows in minutes
- Real-time progress tracking with error logging
Advanced Schema/Data Mapping
- SQL Table ↔ MongoDB Collection mapping (rename, merge, split)
- SQL Column ↔ MongoDB Field mapping (custom naming, ignore fields)
- Auto Conversion: SQL → MongoDB (VARCHAR→String, INT→Number, DATETIME→ISODate)
- Support Complex Types: BLOB→Binary, JSON→BSON, XML→String
Secure & Reliable
- Local Processing: No SQL data uploaded to third-party servers
- SQL Syntax Validation: Auto-detect and skip invalid SQL statements
- Duplicate Data Handling (skip/overwrite/update)
- Scheduled automated imports (daily/weekly/monthly)
Common Use Cases for SQL to MongoDB Import
Database Migration
Migrate legacy SQL databases (MySQL/Oracle/SQL Server/PostgreSQL) to MongoDB for modern application development. Preserve schema structure during migration.
Analytics Data Integration
Import filtered SQL query results to MongoDB for advanced analytics and reporting. Leverage MongoDB's flexible schema for unstructured data analysis.
Historical SQL Data Archiving
Archive old SQL backup files (.sql) to MongoDB for centralized storage and easy querying. Preserve original data types and table relationships.
Test Environment Setup
Import production SQL data to MongoDB development/testing environments. Filter sensitive data and adjust schema mapping for testing needs.
Frequently Asked Questions About SQL to MongoDB Import
Which SQL databases are supported for import to MongoDB?
We support .sql backup files from all major SQL databases: MySQL, Oracle, SQL Server, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, SQLite, DB2, and more.
Does it support complex SQL data types like BLOB/JSON/XML?
Yes — BLOB data is imported as MongoDB Binary type, SQL JSON columns as BSON documents, and XML as String type. You can configure custom conversion rules for any complex SQL data type in the import settings.
Can I import large SQL files (10GB+) without performance issues?
Absolutely! The tool uses stream processing to read SQL files in chunks, avoiding memory overflow. Large datasets are imported in batches, with real-time progress tracking and automatic retry for failed records.
Can I import only specific rows from a SQL table to MongoDB?
Yes! You can execute custom SELECT queries with WHERE clauses to filter data before import (e.g., import only 2024 sales data). The tool also supports LIMIT/OFFSET for partial table imports.
Can I schedule automated SQL to MongoDB imports?
Yes! Save your import configuration as a .bat (Windows) or .sh (Linux/macOS) file, and schedule it using Windows Task Scheduler or Linux Crontab. Perfect for daily/weekly sync between SQL databases and MongoDB.
Ready to Import SQL to MongoDB Effortlessly?
Download SQL to MongoDB Importer (FileToMongo) and streamline your data migration, entry, and archiving workflows with secure, high-performance SQL imports.
Download FileToMongo Free Trial Buy FileToMongo - Starting at $75