Sometimes, you need to convert SQL insert statement to SQL update statement, you can use Withdata DataFileConverter, easy and fast.
For example, you have a file employees_insert.sql, contains 2 SQL insert statements for SQL Server:
insert into employees (department_id,last_name,first_name,job_id,salary,email,manager_id,commission_pct,phone_number,employee_id,hire_date) values (90,'King','Steven','AD_PRES',24000,'SKING',null,null,'515.123.4567',100,'6/17/1987') ; insert into employees (department_id,last_name,first_name,job_id,salary,email,manager_id,commission_pct,phone_number,employee_id,hire_date) values (90,'Kochhar','Neena','AD_VP',17000,'NKOCHHAR',100,null,'515.123.4568',101,'9/21/1989') ;
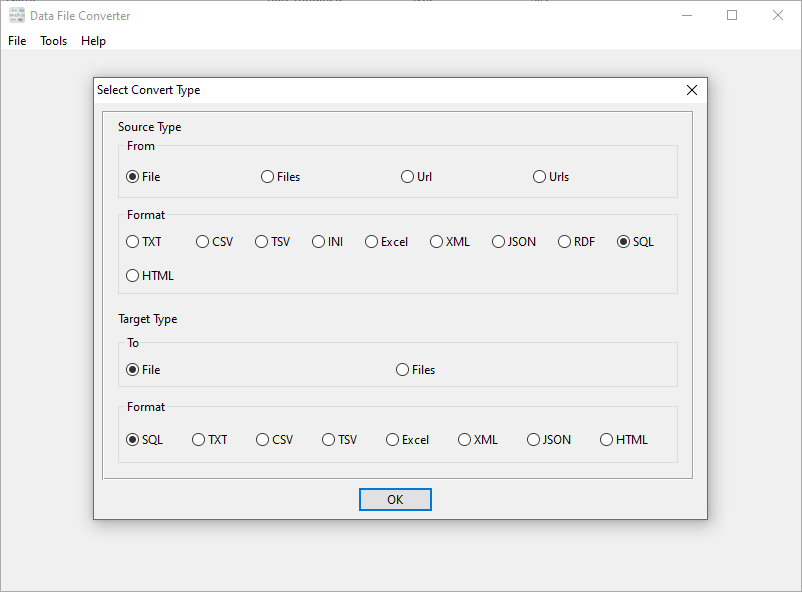
Use DataFileConverter, start a new task, and choose “From” “File” “SQL”, “To” “File” “SQL”.
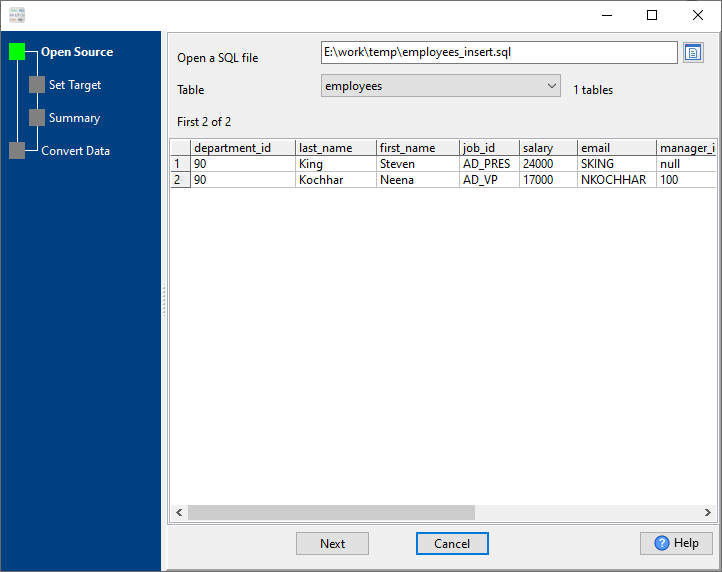
1. Choose source SQL insert statement file.
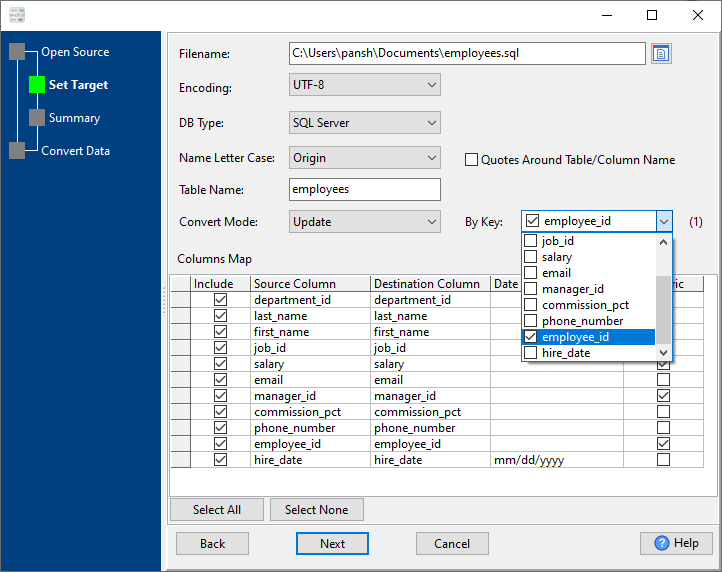
2. Choose “SQL Server” in “DBType”; Choose “Update” in “Convert Mode”; Set “By Key” to primary key, or unique index (include Multiple-Column index).
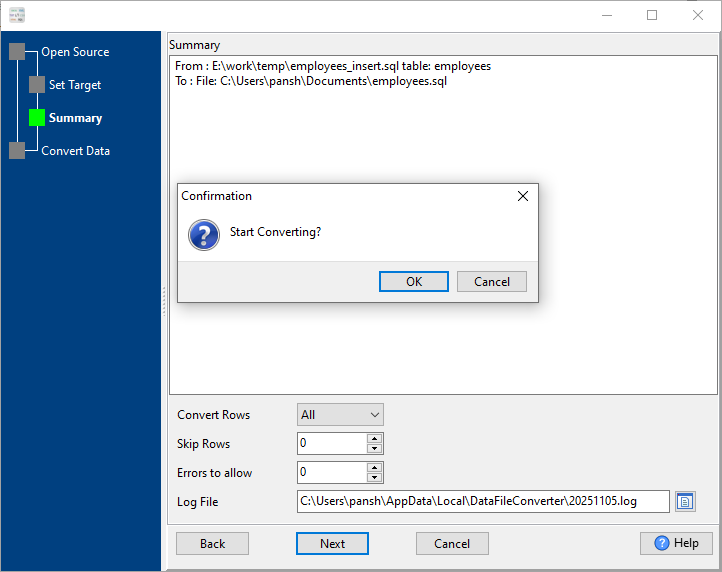
3. See summary, click “Next”, then click “OK” to confirm.
4. See converting, and then click “View” to see output “Update” SQL.
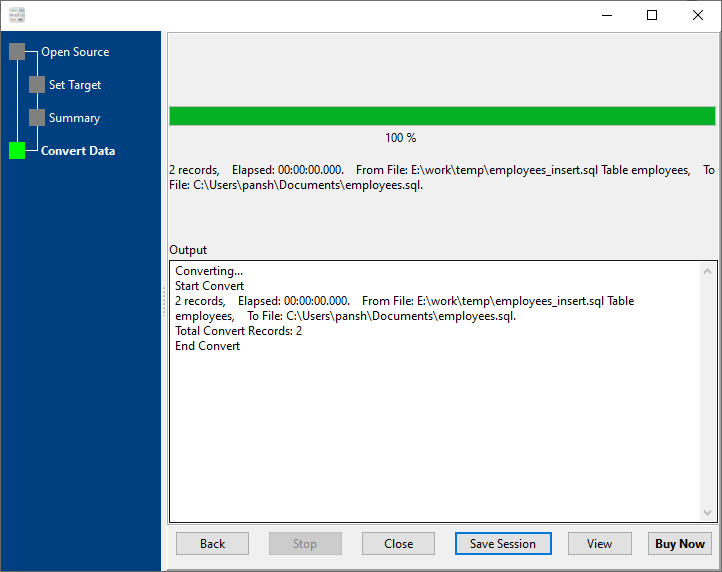
The output “Update” SQL:
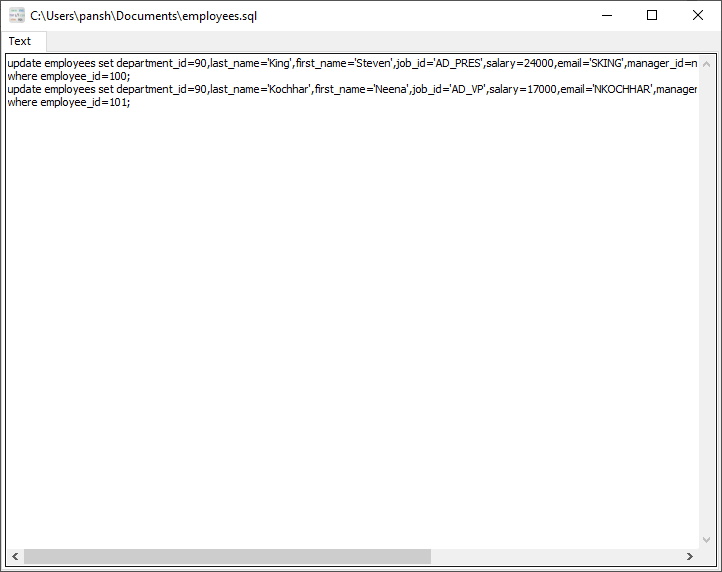
The output “Update” SQL is for SQL Server:
update employees set department_id=90,last_name='King',first_name='Steven',job_id='AD_PRES',salary=24000,email='SKING',manager_id=null,commission_pct=null,phone_number='515.123.4567',hire_date='6/17/1987' where employee_id=100; update employees set department_id=90,last_name='Kochhar',first_name='Neena',job_id='AD_VP',salary=17000,email='NKOCHHAR',manager_id=100,commission_pct=null,phone_number='515.123.4568',hire_date='9/21/1989' where employee_id=101;
You can convert for other database also, just choose other “DBType”:
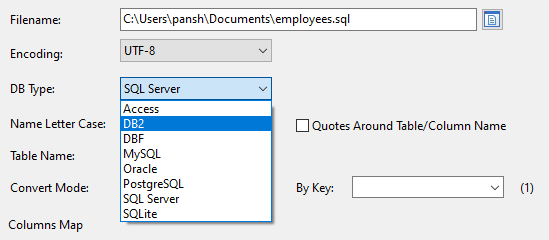
And it will create “Update” SQL for the “DBType”, like DB2:
update EMPLOYEES set DEPARTMENT_ID=90,LAST_NAME='King',FIRST_NAME='Steven',JOB_ID='AD_PRES',SALARY=24000,EMAIL='SKING',MANAGER_ID=null,COMMISSION_PCT=null,PHONE_NUMBER='515.123.4567',HIRE_DATE=TIMESTAMP_FORMAT('6/17/1987','MM/DD/YYYY')
where EMPLOYEE_ID=100;
update EMPLOYEES set DEPARTMENT_ID=90,LAST_NAME='Kochhar',FIRST_NAME='Neena',JOB_ID='AD_VP',SALARY=17000,EMAIL='NKOCHHAR',MANAGER_ID=100,COMMISSION_PCT=null,PHONE_NUMBER='515.123.4568',HIRE_DATE=TIMESTAMP_FORMAT('9/21/1989','MM/DD/YYYY')
where EMPLOYEE_ID=101;
MySQL:
update `employees` set `department_id`=90,`last_name`='King',`first_name`='Steven',`job_id`='AD_PRES',`salary`=24000,`email`='SKING',`manager_id`=null,`commission_pct`=null,`phone_number`='515.123.4567',`hire_date`=str_to_date('6/17/1987','%m/%d/%Y')
where `employee_id`=100;
update `employees` set `department_id`=90,`last_name`='Kochhar',`first_name`='Neena',`job_id`='AD_VP',`salary`=17000,`email`='NKOCHHAR',`manager_id`=100,`commission_pct`=null,`phone_number`='515.123.4568',`hire_date`=str_to_date('9/21/1989','%m/%d/%Y')
where `employee_id`=101;
Oracle:
update EMPLOYEES set DEPARTMENT_ID=90,LAST_NAME='King',FIRST_NAME='Steven',JOB_ID='AD_PRES',SALARY=24000,EMAIL='SKING',MANAGER_ID=null,COMMISSION_PCT=null,PHONE_NUMBER='515.123.4567',HIRE_DATE=to_date('6/17/1987','MM/DD/YYYY')
where EMPLOYEE_ID=100;
update EMPLOYEES set DEPARTMENT_ID=90,LAST_NAME='Kochhar',FIRST_NAME='Neena',JOB_ID='AD_VP',SALARY=17000,EMAIL='NKOCHHAR',MANAGER_ID=100,COMMISSION_PCT=null,PHONE_NUMBER='515.123.4568',HIRE_DATE=to_date('9/21/1989','MM/DD/YYYY')
where EMPLOYEE_ID=101;
PostgreSQL:
update employees set department_id=90,last_name='King',first_name='Steven',job_id='AD_PRES',salary=24000,email='SKING',manager_id=null,commission_pct=null,phone_number='515.123.4567',hire_date=to_timestamp('6/17/1987','MM/DD/YYYY')
where employee_id=100;
update employees set department_id=90,last_name='Kochhar',first_name='Neena',job_id='AD_VP',salary=17000,email='NKOCHHAR',manager_id=100,commission_pct=null,phone_number='515.123.4568',hire_date=to_timestamp('9/21/1989','MM/DD/YYYY')
where employee_id=101;
SQLite:
update [employees] set [department_id]=90,[last_name]='King',[first_name]='Steven',[job_id]='AD_PRES',[salary]=24000,[email]='SKING',[manager_id]=null,[commission_pct]=null,[phone_number]='515.123.4567',[hire_date]='1987-06-17' where [employee_id]=100; update [employees] set [department_id]=90,[last_name]='Kochhar',[first_name]='Neena',[job_id]='AD_VP',[salary]=17000,[email]='NKOCHHAR',[manager_id]=100,[commission_pct]=null,[phone_number]='515.123.4568',[hire_date]='1989-09-21' where [employee_id]=101;
See also:
Export databases data to SQL files
Convert data between SQL and other file types
Import data from SQL files to databases